Exploring the rural-urban continuum: how to define Functional Rural Areas in the context of rural transitions?
Introduction to RUSTIK’s Deliverable D1.1 “Methodological Framework to Define Functional Rural Areas and rural transitions”
The RUSTIK project published its first deliverable, “Exploring the rural-urban continuum”. This methodological framework, developed by the Council for Research in agricultural economics (CREA), Italy, and the Countryside and Community Research Institute (CCRI), UK, aims to define Functional Rural Areas and propose a new approach to their classification.
Why is there a need for a new classification of Rural areas?
To make rural areas ready to adapt to changes it is important to understand how different drivers and trends impact rural areas, and how they respond to change. Hence the need to develop a conceptual framework that explains rural areas’ capacity to respond to the socio-economic/demographic, environmental/climate and digital aspects. It is important to develop a place-based path and scale up successes at a local level, with appropriate facilitation from national, regional, and local governments.
By enhancing our understanding of the diverse functionalities, unique characteristics, and possible future scenarios of rural areas, the RUSTIK project will be able to provide more effective strategies, initiatives, and policies that promote sustainable transitions in rural areas.
What are rural functional areas? A five-step approach.
Differences exist in defining the term “functional” for rural areas, with shifting criteria and less emphasis on agriculture. The term has varied meanings based on disciplinary and institutional contexts, with a historical urban bias. Efforts are being made to address this bias and recognize the important societal functions provided by rural areas.
There are several approaches to define functional rural areas. Studying functional relations in the case of rural areas implies focusing on the role that the countryside can play in production, consumption and ecosystem functions, not only for nearby urban areas but also for the broader society and in relation to national and international markets, institutions and business actors. It also implies using mixed approaches based on information available at the most granular level or municipal units.
Based on these assumptions, to define functional rural areas, a five-step classification can be made (Fig 1)
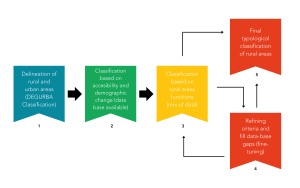
The new classification system will be tested in fourteen Pilot Regions. This process will ensure that the classification is robust and develop an advanced understanding of the Pilot Regions’ characteristics, functionalities and capacities in participating in the next steps of the RUSTIK project.
Diversity of rural areas and their capacity to face transitions
The transitions happening in rural areas are influenced by various drivers and trends, including socio-economic/demographic, environmental/climate, and digital factors. These transitions have the potential to impact the response capacities, territorial capital, and social capital of each rural area. Understanding these drivers and trends is crucial for effective policy development and implementation.
Europe is grappling with an aging population, which is expected to worsen in the coming decades. This leads to disparities between regions, amplified by variations in labour markets, access to services and infrastructure, market power distribution, and the digital divide.
Addressing environmental and climate challenges requires collaborative efforts that go beyond national borders. Policies like the Common Agricultural Policies, Green Deal, and Biodiversity Strategies are crucial in combating these issues. While EU-level targets are important, tangible actions and physical changes must be implemented at the local and regional levels.
The digital transition has the potential to exacerbate existing inequalities and create new divisions, particularly in rural areas. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the discrepancies between urban and rural regions, especially in terms of digital access. It is essential for rural communities to develop basic and professional digital skills to participate in the future job market and society. Economic factors, demographics, and limited connectivity further contribute to the digital skills gap.
To effectively respond to these transitions in rural areas, policies need to be tailored to specific needs and places. The delivery of policies is also crucial for their successful implementation. Several steps can be taken to enhance the capacity of rural areas to respond:
- Identify transition needs: Conduct a thorough analysis to understand the challenges and needs associated with the transition, considering social, economic, and environmental factors.
- Develop an enabling policy environment: Create policies that empower local actors and communities to make choices aligned with desired outcomes. Provide necessary resources, information, and support for effective decision-making and implementation.
- Promote the emergence of new institutions and groups: Encourage the formation of local organizations, networks, and collaborations to address challenges associated with the transition.
- Enhance policy delivery: Ensure clear communication, accessible information, and efficient mechanisms for policy implementation. Involve local stakeholders to increase ownership and involvement.
- Integrate macro-economic context and policy system: Recognize how macro-drivers and trends at the international level can create risks and opportunities at different territorial levels. Align policies with broader macro-economic goals and incorporate measures to mitigate risks and harness opportunities.
- Targeted policies for transition challenges: Develop specific policies to facilitate and enable transition possibilities and pathways, including regulations, incentives, advice/information campaigns, and other supportive measures.
- Focus on sensitive territories: Pay special attention to territories with limited resources or accessibility issues. Design policies that cater to their unique needs, implementing localized systems of incentives and support mechanisms to encourage participation and resilience.
By adopting this comprehensive approach to policy development and delivery, the capacity to respond to transitions can be enhanced, leading to smoother and more effective transitions in social, economic, and environmental domains.
For further information, you can access the full report at https://rustik-he.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/RUSTIK_D-1-1_Methodological_Framework_31.03.23.pdf

