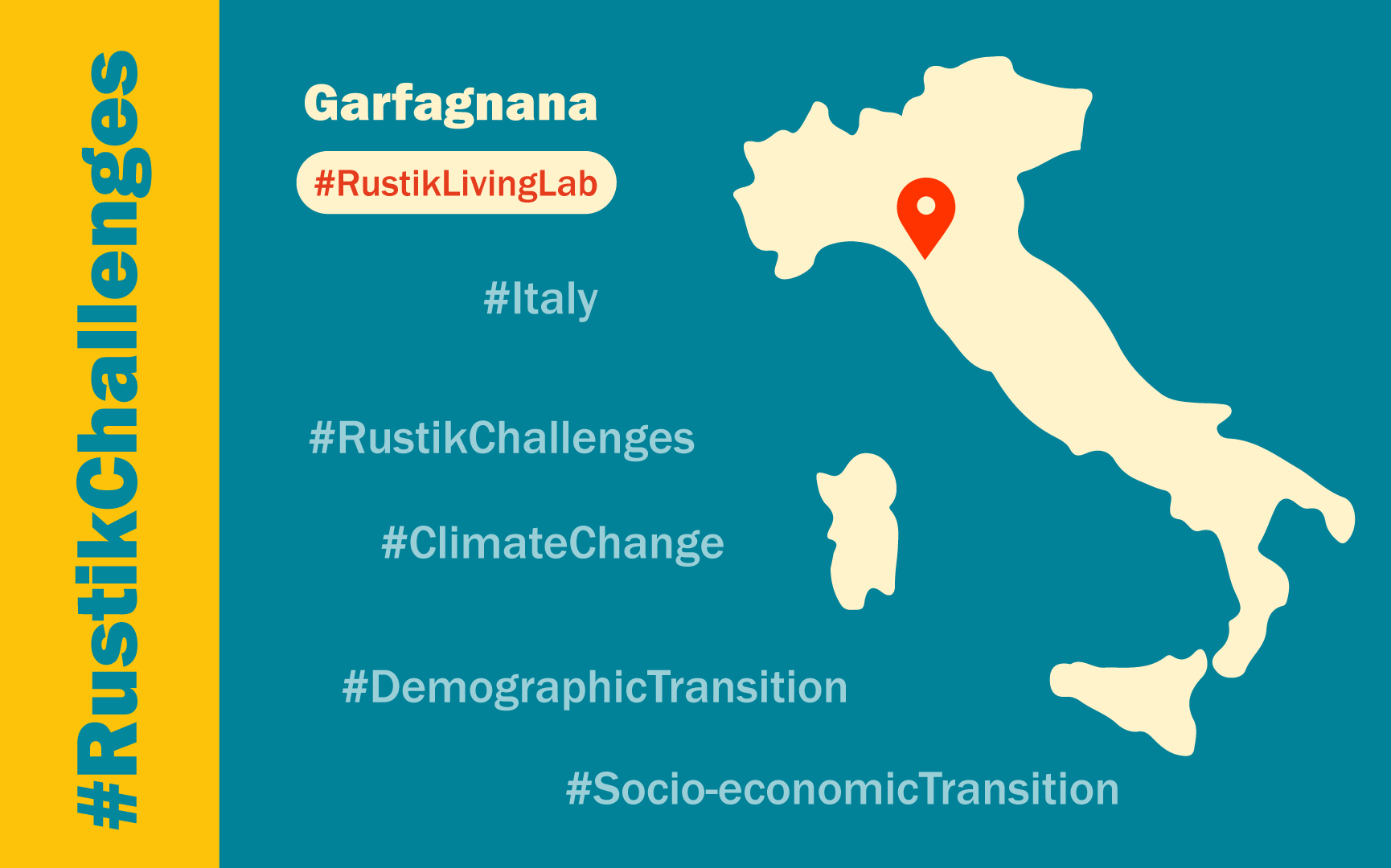
Nestled in the northern part of Tuscany, the Garfagnana region, comprising Media Valle del Serchio, Alta Versilia, and Appennino Pistoiese, stands as a picturesque landscape covering 2110 km2. The area, home to 27 municipalities, is under the purview of LAG Montagnappennino, the driving force behind the LEADER programme. As we delve into the complexities of Garfagnana, we uncover a rich tapestry of socio-economic, demographic, climate, and environmental transitions.
Socio-economic and Demographic Transition:
At the heart of Garfagnana’s challenges lies the persistent issue of depopulation. From 2011 to 2020, the region experienced a concerning -7.58% decrease in total population. Distinct challenges include uneven distribution of commercial services, generational renewal hurdles, a less attractive environment for new investments, historic center degradation, limited accessibility to services for non-capital residents, and entrepreneurial gaps in the social sector. To address these, a multifaceted approach is essential, focusing on social capital, community regeneration, and innovative models for local development.
Climate and Environmental Transition:
With a landscape dominated by forests (88% coverage in 2020), Garfagnana’s natural wealth is both a strength and a vulnerability. The majority comprises mature forests (86%), witnessing a 15% growth between 2013 and 2020. Balancing sustainable forest use for productivity and preventing uncontrolled forest spread due to abandonment emerges as a critical challenge. Recognizing the multifunctionality of forests is imperative, transforming them into sources of recreation, climate change mitigation, and cultural significance. Civic uses, particularly through local forest cooperatives, are vital for harmonizing the needs of both the community and the environment.
Living Lab Challenge:
Garfagnana’s Living Lab confronts the intertwined challenges of socio-economic and environmental transitions. Community projects emerge as a beacon of hope, fostering cooperation, strengthening social capital, and building synergies between local initiatives. The focus on civic uses and multifunctional forest models aims to create a balance between social and environmental goals. The region’s response to the COVID-19 emergency showcases the potential of community-driven regeneration projects, aligning with the goal of preserving social capital and revitalizing local communities.
Rationale:
The symbiotic relationship between socio-economic and environmental transitions becomes evident in Garfagnana’s response to the COVID-19 crisis. The MontagnAppennino LAG, acting as a pillar of social cohesion, initiated community regeneration projects to stimulate development ideas and enhance the quality of life in rural territories. The key lies in creating and increasing social capital, an essential element in retaining the local population. Simultaneously, the region recognizes the potential of its vast forest cover, focusing on sustainable forest use, climate change mitigation, and ecosystem service recognition.
Policy Relevance: With upcoming LEADER programming and participation in the National Strategy for Inner Areas, Garfagnana sees an opportunity to solidify and support pilot experiences arising from community regeneration projects and forest-focused initiatives. Data and analysis play a pivotal role in guiding ongoing processes, adapting future actions, and providing a foundation for governance choices. Collaboration with regional authorities and self-evaluation processes is crucial for demonstrating the effectiveness of actions to the European Union.
Research Questions:
- How can sustainable forest use be promoted to support local added value and prevent uncontrolled forest spread?
- What role do community projects play in fostering cooperation, strengthening social capital, and building synergies between local initiatives?
Emerging Data Needs:
- Comprehensive knowledge of forest stock, ownership structure, and management plans.
- In-depth understanding of qualitative dimensions like social capital, trust, and reciprocity.
- Monitoring immigration and policies attracting new residents.
- Data collection on third-sector projects and their socio-economic impacts.
Data Availability:
- Adequate regional and national data for forest heritage characteristics.
- Existing data on qualitative dimensions but a need for case studies on community regeneration.
- Collaboration with IRPET for socio-economic, demographic, and public expenditure data.
Garfagnana’s transition journey is a testament to the intricate balance needed between human and environmental well-being. As the Living Lab unfolds, it becomes a living example of how data, collaboration, and innovative approaches can pave the way for a sustainable and vibrant future.
Stay tuned for updates on this captivating journey into the heart of Tuscany!